In Japan and Korea, Mobile Content Makes Money
Even mobile e-commerce – which has been a bust elsewhere – is starting to take off in Japan. More than a third of mobile Net subscribers have used their phones to buy such goods as CDs and concert tickets, according to the Mobile Content Forum, an industry trade group.

 If you’re going to build one of those tiny i-mode websites or create a downloadable Java application (Games, anyone?), then you’re going to have to test your software before going live – and that means using emulator tools. If you don’t, you have to use actual handsets for testing and the packet fees would wipe out even the fattest bank account. We visit leading provider Zentek, and then speak with Tokyo University expert Dr. Sam Joseph – who has a lot of experience in making emulators actually emulate. Want to know what portion of a mobile project’s costs are consumed by testing prior to launch? Watch this one.
If you’re going to build one of those tiny i-mode websites or create a downloadable Java application (Games, anyone?), then you’re going to have to test your software before going live – and that means using emulator tools. If you don’t, you have to use actual handsets for testing and the packet fees would wipe out even the fattest bank account. We visit leading provider Zentek, and then speak with Tokyo University expert Dr. Sam Joseph – who has a lot of experience in making emulators actually emulate. Want to know what portion of a mobile project’s costs are consumed by testing prior to launch? Watch this one. G-mode was set up in 2001 for the sole purpose of creating Java games for wireless. They say they’ve sold 63 million downloads since then, and their games are played 250,000 times per day. This is the first mobile content provider we’ve ever met that claims made-in-Japan games can be exported overseas, despite the barriers of language and culture. Considering that Tetris — known globally — has no text, they just could be right.
G-mode was set up in 2001 for the sole purpose of creating Java games for wireless. They say they’ve sold 63 million downloads since then, and their games are played 250,000 times per day. This is the first mobile content provider we’ve ever met that claims made-in-Japan games can be exported overseas, despite the barriers of language and culture. Considering that Tetris — known globally — has no text, they just could be right.  With over 150 different Internet-capable cellular handsets in use by four different carriers, the challenge of formatting content to match the terminal is becoming, well, terminal. Each model has its own screen dimensions, color capability, and other idiosyncrasies, and if your business depends on making sure that mobile shoppers can see pics of all your products, like, say Yahoo Japan Auctions’ does, you’re in a world of hurt. Fortunately, one company has a solution. Thank God for the Americans!
With over 150 different Internet-capable cellular handsets in use by four different carriers, the challenge of formatting content to match the terminal is becoming, well, terminal. Each model has its own screen dimensions, color capability, and other idiosyncrasies, and if your business depends on making sure that mobile shoppers can see pics of all your products, like, say Yahoo Japan Auctions’ does, you’re in a world of hurt. Fortunately, one company has a solution. Thank God for the Americans! 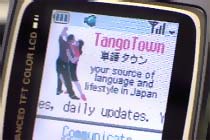 Tango Town — a recently launched J-Sky wireless Web site — works as well with Japanese fonts, characters, and data encodings as with English.
Tango Town — a recently launched J-Sky wireless Web site — works as well with Japanese fonts, characters, and data encodings as with English.